The incident in a mid-sized organisation in Myanmar started with “strange slowness” on a few internal systems. User logins took longer than usual, some applications stopped responding, and shared folders returned random errors. When the IT team checked key servers, they discovered that important data files had been renamed with the extension .BAFAIAI. and ranom note read_this_to_decrypt_files.html In that moment, it became clear that BAFAIAI Ransomware was actively attacking the environment and that several critical servers were at risk.
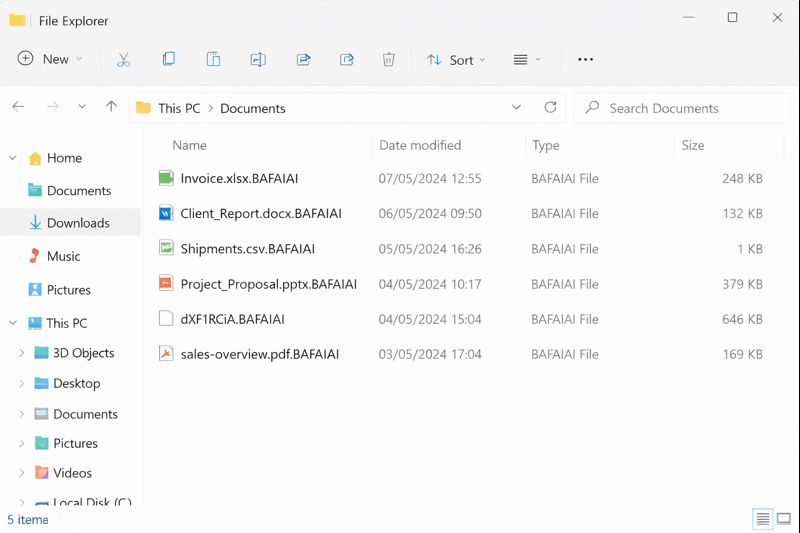
From there, the difference between a full operational collapse and a controlled recovery depended on what the team did in the next 24 hours.
How BAFAIAI Ransomware Impacted Key Servers in Myanmar
BAFAIAI focused on the servers that mattered most to daily operations:
- Application servers that handled orders, internal workflows, or customer requests.
- File servers that stored shared reports, exports, and important documents.
- Some database-related directories that supported dashboards and internal tools.
As a result:
- Frontline staff could not reliably access the systems they used to serve customers.
- Managers lost visibility into current activity because key reports failed.
- Scheduled tasks and integrations started silently failing in the background.
The infrastructure was still powered on, but practically, the business was losing control of its core data.
Containment First, Not Quick “Fixes”
Instead of rushing into random tools or reboots, the team in Myanmar made containment their first priority.
They immediately:
- Disconnected affected servers and storage from the network to stop lateral movement.
- Disabled non-essential remote access paths and old admin accounts.
- Alerted staff not to open suspicious files or attempt self-made “repairs”.
- Preserved critical logs and a small set of encrypted samples for later forensic analysis.
These actions prevented BAFAIAI Ransomware from spreading into additional servers, endpoints, and backup devices that were still clean. At the same time, they kept the environment stable enough for proper investigation.
Explaining the Situation to Management in Business Terms
Next, IT and operations prepared a short, clear summary for management. The goal was to give leadership a realistic picture of impact and options.
They focused on:
- What is affected now: key application servers, some file shares, and parts of the reporting layer.
- What still works: email, some cloud platforms, and basic communication channels.
- Risks if mishandled: extended downtime, financial losses, client dissatisfaction, and long-term trust issues.
This framing allowed management to make informed decisions: supporting a structured recovery plan, approving temporary workarounds for customers, and avoiding knee-jerk reactions like instantly paying ransom.
Technical Assessment and Bringing in Specialists
Once containment and communication were in place, the team moved into a structured technical assessment.
They mapped:
- Which servers and paths were encrypted and which remained unaffected.
- Where data truly originated (databases, external systems, data warehouses).
- How backups were configured, including any offline or offsite copies.
Encrypted samples and log data were reviewed. The organisation then contacted specialist responders through FixRansomware.com and submitted sample files via app.FixRansomware.com for deeper analysis of BAFAIAI Ransomware and potential recovery routes.
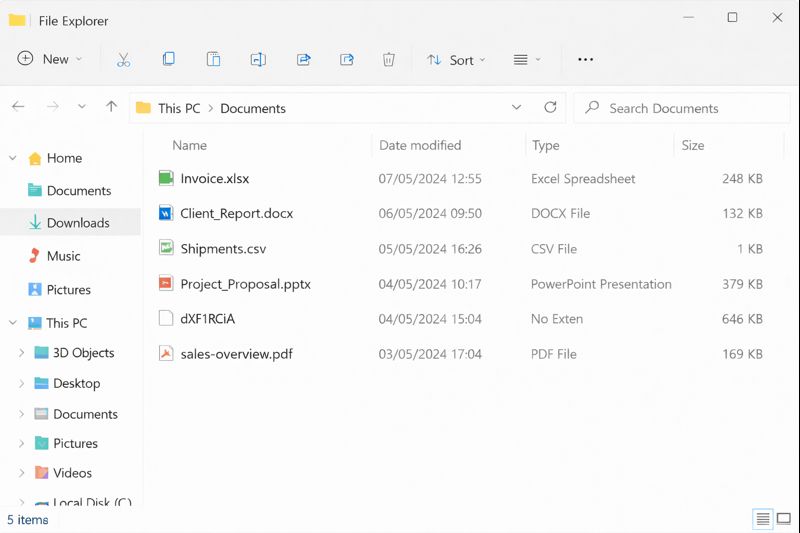
For overall strategy, the team aligned with the official CISA Ransomware Guide (CISA/MS-ISAC Ransomware Guide), which stresses isolation, structured analysis, and restoration from trusted backups rather than blind negotiation.
Building a Recovery Plan to Bring Critical Data Back Online
With more clarity, the company and external experts designed a focused recovery plan.
Key steps:
- Clone affected volumes before changes
The team created sector-level clones of the disks that hosted critical data. All tests and potential decryption attempts were performed on clones, protecting original disks as a last-resort fallback. - Identify clean backups and alternative data sources
Backups stored offsite or on separate media were checked and validated. Clean restore points became the foundation to bring key servers back online. Where backups were incomplete, the team also looked at exports, partner data, and other copies. - Restore systems based on business priority
Servers that directly supported revenue, customers, and core operations were restored first. Internal or low-priority services were postponed to later phases. - Rebuild missing data where necessary
For time windows not fully covered by backups, data was reconstructed from email attachments, external integrations, and still-healthy client-facing systems. All manual adjustments were documented for audit and quality control. - Validate each restored component
Before fully reopening access, core workflows were tested by key users. Only after those checks passed did the company gradually reconnect more users and services.
Lessons from a BAFAIAI Ransomware Attack in Myanmar
In the end, the organisation in Myanmar successfully brought critical data and systems back online without paying ransom. The BAFAIAI Ransomware incident highlighted several key lessons:
- Key servers must have robust, tested backup strategies that include at least one offline or immutable layer.
- Remote access and privileged accounts should be tightly controlled, monitored, and reviewed regularly.
- A concise incident response playbook, shared across IT, operations, and management, greatly reduces confusion and reaction time.
The attack showed how aggressively BAFAIAI Ransomware can hit key servers—but it also proved that disciplined containment, clear communication, and expert-guided recovery can restore operations and strengthen resilience for the future.


